
Pain in the king's meadow is a common Symptom and indicates difficulties in the body – the occurrence of joint disorders or just increased Stress on the feet.
Hard to find, someone who will never experience pain in the knees in a certain period of life. Complaints, Flicks or pain of varying intensity in the knee joints than in adults, and in children by a variety of reasons. The older you get, the higher the likelihood of various diseases, of which the first character is a pain in the knees is is. This happens due to the age-related peculiarities of the organism: the slowing down of the metabolic processes, the wear and tear of the cartilage of the joints, of the accession of other problems with the musculoskeletal system, vessels, nerves.
Due to the complex anatomical structure, a variety of structures and high loads, experienced and often and overload the knee joints are very vulnerable. The damage done to one element of the structure, such as a mucus bag, leads to a violation of the motor function of the knee and, accordingly, pain syndrome. Ligaments and menisci are the most vulnerable, she was hurt in 80-85% of cases.
The anatomical structure of the knee
The Bottom consists of a knee joint, the distal end of the Femur with two condyles and podmienkami, Tibia tubular bone, muscles, nerves, blood vessels, ligaments, Patella (Patella), menisci, joint capsules, and.
The knee joint is one of the most important joints of the body. From above him, the leg fits. Articular surfaces of their lateral (outer) and medial (internal) condyle to articulate with the patella and Tibia-bone use. Menisci, which serve as the connective tissue of cartilage as a shock absorber of the joint. Thanks to the reasonable weight happens distribution on the tibial Plateau, and increases the stability of the joint. Thin, two-headed, paliperidonesee and other muscles to synchronize the capsule-ligamentous structure, whereby the motor function of the knee joint.
Elements of the knee with each other many of the bands are connected. Inside the knee joint there are two ligaments – the front and back. Podmyshalsky bedernau bone benefits associated with the peroneal and posterior tibial collateral bone use tapes. Oblique knee flexor bundle is located in the rear part of the Bursa in the knee joint. A series of joint cavities, the Start – synovial on capsule mark, not with the joint communicate. Blood supply of the elements of the knee is a useful complement to the fine network of blood vessels and Innervation – nerve fibers.
Causes of pain in the king's meadow
There are many causes for pain in the joints of the king's meadow, which can be roughly divided into several groups.
Traumatic Lesions Of The Elements King's Meadow:
- A contusion of the knee. As a result of the rupture of the vessels, local bleeding in the soft tissues of the joint. Redness, swelling, injury of the nerve endings leads to pain, obstruction of the movement.
- Complete or partial rupture of the ligament. More common is a partial violation of the integrity of the inner lateral bands from excessive Eversion of the lower leg to the outside.diagnosed
Outer bundle of tears rare in comparison to internal. This happens due to the strong deviation of the lower leg to the inside, the in exposure of the feet, for example. Rupture of the cruciate ligaments, inevitably, is accompanied by a hemarthrosis.
Complete rupture of both ligaments often combined with damage to the joint capsule, tear of the inner meniscus. Such Trauma leads to excessive mobility of the knee joint, accompanied by severe pain, the intensity of which depends on the extent of the rupture.
- Hemarthrosis of the knee joint – the outpouring of blood into the cavity of the joint. Sometimes traumatic and non-traumatic character. Traumatic hemarthrosis occurs with tears of the menisci, complete or incomplete, of the ligaments, intra-articular fractures, bruises of the king's meadow cracks. Non-traumatic variant is a Symptom of diseases characterized by increased brittleness of the vessel wall, or impaired blood clotting. To do this, haemophilia, scurvy, severe hemorrhagic diathesis to count. As a result, the exhaust gas temperature increases in the joint cavity of blood squeezed out of the tissue, the disruption of the blood flow in them. A special Pigment is hemosiderin – negative effect on the ligaments, cartilage hyaline, synovial bag, resulting in a loss of their elasticity. The result of a lesion of the articular surface of the Bursa, the swelling of your villi and increased production of synovial fluid. The result of the repeated bleeding, the Degeneration and destruction of the joint will.
- Patella mini scope – a violation of the integrity of the menisci of the knee joint. In the case of the lateral shape, is damaged, the outer meniscus, when the medial (inside). This is one of the most common, but difficult to diagnosable damage to the knee joint. In the Zone of the risk of the disease, only the athletes with intense training sessions, but also the ordinary people are not. The meniscus tear to occur of unusually sharp movements when turning the hull, the exposure of legs, a strong blow to the king's meadow.
- Dislocation of the Patella – pathological dislocation of the kneecap. Trauma not diagnosed more than 0.7% of the cases of the total number of dislocations. The most common external dislocation occurs, and more rarely – very rarely vertical or torsional. In the case of incomplete dislocation of the patella is determined on the lateral (outer) condyle, with the complete outside of the lateral condyle.
- Closed or open fractures of the knee joint and of the upper part of the bone, use of the lower leg or the lower Department of bedernau bone use. Such injuries often combined with soft tissue injuries of the knee, causing massive bleeding, the excessive mobility in the area of the knee, its Deformation.
Inflammatory and degenerative-dystrophic diseases of joints of elements of the knee:
- Arthritis inflammatory lesion of the joint of the knee. Similar to the Mechanisms of the development of the pathology of ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid Arthritis, gout (deposition of uric acid in the joints) observed in osteoarthritis.
- Osteoarthritis (gonarthrosis) with lesions of the knee joint of non-inflammatory type of, that all of his structures and leads to severe degenerative changes.
- Bursitis inflammation of the synovial Bursa leads to pain in flexion-extensor movements in the king's meadow.
- Periarthritis of the tendons of the knee joint inflammation of the capsule-goose-feet, king's meadow-the tendons and the muscles and ligaments around the joint. The pain occurs mainly during the descent on the stairs, especially with a heavy load, and is concentrated on the inner side of the knee.
- The chondropathy Patella – degenerative-necrotic changes of the articular cartilage (the back) of the patella. The degree of destruction may be different from the areas of the lung abrasion soften up cracks and complete.
- Chondromatous – a serious chronic disease, due to a dysplastic process with island and degeneration phases of the membrane shell in the joint cartilage of chondrome. There is ossification of the single cartilage-Tel is not excluded.
- A-Baker-cyst – the formation of a dense elastic rounded tumour formation in the popliteal Fossa, is located on the opposite side of the patella. The cyst is clearly visible in the unbent condition of the knee. Discomfort, causing pain in the area of the Vena poplitea. With significant amounts of the blood vessels and nerves, leading to disruption of Innervation and circulation.
- The disease von hoff disease, accompanied by the defeat and the further degeneration of the adipose tissue located around the knee joint. Herniation, edema, and other damage to the fat cells – adipocytes – tissue Substitution of dense connective. In effect, a buffer zone function, "fat-pad" not be disturbed, even the fat tissue is in the situation, the role of the shock absorber.
- The Osgood–Schlatter disease – pathology, characterized by necrosis process nubby part of the Tibia. Diagnosed in adolescents from 10 to 18 years of age with the Sport. Below the kneecap, painful bump will appear, if untreated, leads to restriction of the movement of the legs or complete immobilization, malnutrition, as well as muscles.
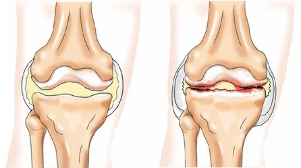
Diseases in which the possible radiating pain in the area of the king's meadow:
- Coxarthrosis of the hip – chronic lesion of the hip joint, accompanied by a progressive Degeneration and degenerative changes in him. Often the pain is spreading down to the outside of the thigh up to the king's meadow or down.
- Neuropathy of the sciatic nerve – the non-inflammatory lesion of the nerve as a result of the compression or spazmirovannah blood vessels. This nerve goes down to the soles of the feet, starting in the lumbar area and the coccyx and pelvis. Blockage in a point on his course leads to disruption of the sensitivity or throbbing pain.
- Fibromyalgia – extra-articular defeated soft tissues non-inflammatory character with the totality of the symptoms in the Form of joint pain, muscle weakness, Depression, etc.
Some systemic diseases that cause pain in the knees:
- Osteoporosis – a disease of the skeletal system chronic progressive currents, mineral composition and bone density. "Washout" of calcium from the bone, make use of leads to their embrittlement. The process is accompanied by aching pain or pain in the extremities.
- Tuberculosis of the bone use. Tuberculous lesions of the Phase of bone benefits will lead to constant severe pain.
- Osteomyelitis – disease infectious-inflammatory nature, which all the structural elements of bone to use. The result as a specific, e.g., tuberculous, and so non-specific, often coccal, Osteomyelitis is the use of hyperemia of the skin, swelling, local sharp pain in the bone and muscles, febrile temperature.
- Some Infectious Diseases. When Reiter's syndrome, with the exception of the participation in the urogenital tract and the mucous membranes of the eyes, of the affected joints skin. One of the manifestations of Lyme disease is arthralgia.
Types of pain in the knees
Depending on the etiology of the character and the intensity of the pain can be different.
- Oppressive. In The Case Of Arthritis, Osteoarthritis.
- Acute, strong. In the case of fractures elements of king's meadow, fraction strips, acute Bursitis, king's meadow-injury, aggravation of a mini-scope, deforming osteoarthrosis.
- Throbbing. While Osteoarthritis osteoarthritis, injuries of the meniscus.
- Drilling. Osteomyelitis.
- Dull. In the case of Bursitis, chronic, of the Legg.
- Fry. By the compression of the sciatic nerve, tuberculous process in the bone use.
- Shoot. In the case of tension in the nerve trunk.
- Pain when walking. In the case of the Baker cyst, Bursitis, Arthritis, gonarthrosis, periarthritis.
- Pain at rest. In The Case Of Gout, Arthritis.
Diagnosis of pathologies, the pain in the knees
Fizikalna Investigation:
- Medical history and complaints;
- visual inspection with Palpation of the knee.
Laboratory tests:
- biochemical and clinical blood tests;
- serological blood analysis;
- immunological blood tests;
- rheumatologic test;
- bacteriological examination of synovial fluid.
Invasive instrumental methods:
- Arthroscopy;
- Puncture of the joint capsule;
- Puncture, Biopsy Bone Use.
Non-invasive instrumental diagnosis:
- x-ray of the knee joint;
- densitometry;
- Ultrasound examination of the joint;
- MRI or CT.
Treatment of pain in the knees
If the pain is of traumatic nature do not occur in one or both knees, you should first consult a doctor, the results on the basis of complaints of the patient and the results of the physical examination, to a more narrow specialists – orthopedic surgeons, rheumatologists, the phlebologist, or neurologist. In the case of all injury to the knee need to stomatologist to a surgical or trauma orthopedic surgeons.
The treatment in each case is different, depends on the cause of the pain, that is, from the nature of the injury or illness. For every disease there is a treatment regimen. But for the beginning, the Patient should observe some General rules:
- significantly, the duration of the walks and the stay reduce on the legs in the course of the day;
- Athletes temporarily (until recovery), training, and ordinary people from running or jumping;
- in the case of the amplification of the pain completely movements give up, applied to the king's meadow, fixing Bandage, elastic Bandage;
- you wear a bandage or a Bandage for the immobilization of the knee joint;
- in the cold on the site of the traumatic exposure.
Rheumatoid, psoriatic Arthritis, systemic autoimmune severe complex treatment to diseases, he for many months. Basic therapy consists of immunosuppressive agents, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and hormonal drugs, drugs, and Gold, etc.
In the treatment of Bursitis pain relievers and inflammation-apply-inflammatory drugs. If the infection is diagnosed, a course of antibiotics. Therapeutic puncture of the bags is for the removal of excess fluid from the synovial cavity and/or the introduction of one of your corticosteroids. Of the chronic inflammation of the Bursa surgery – surgical excision of bursae helps.
When deforming osteoarthrosis effective intra-articular injections of corticosteroids, long-term taking of NSAIDs and chondroprotectors. For the decrease of the pain syndrome topically administered, compresses, applications with dimexidum, or bischofite, ointments and gels with anti-inflammatory effects. Massage, Physiotherapy, Physiotherapy Helps. Severe lesions of the knee joint may require surgery arthroplasty joint replacement.
The treatment of osteoporosis consists of a in kursovom admission bisphosphonates, calcitonin, calcium supplements, Vitamin D, etc.
Treatment of torn meniscus can be conservative or surgical. The conservative treatment consists of analgesics, NSAIDs, hyaluronic acid, chondroprotectors. But first of all, produce a position of the joint.
Types of Operation:
- meniskèktomiâ;
- Aplasia (incomplete) meniskèktomiâ;
- Meniscus Transplantation;
- Arthroscopy;
- arthroscopic suture of the rupture of the meniscus.
In the case of all injuries of the knee after the treatment, the period of Rehabilitation is very important, to. under the control of the rehabilitation, or orthopaedic surgeons The doctor is the optimal program is the restoration of the function of the joint. The main methods of post-operative Rehabilitation as Massage and medical gymnastics. Also effective classes, in special simulators, developed gradually in the knee joint.














































